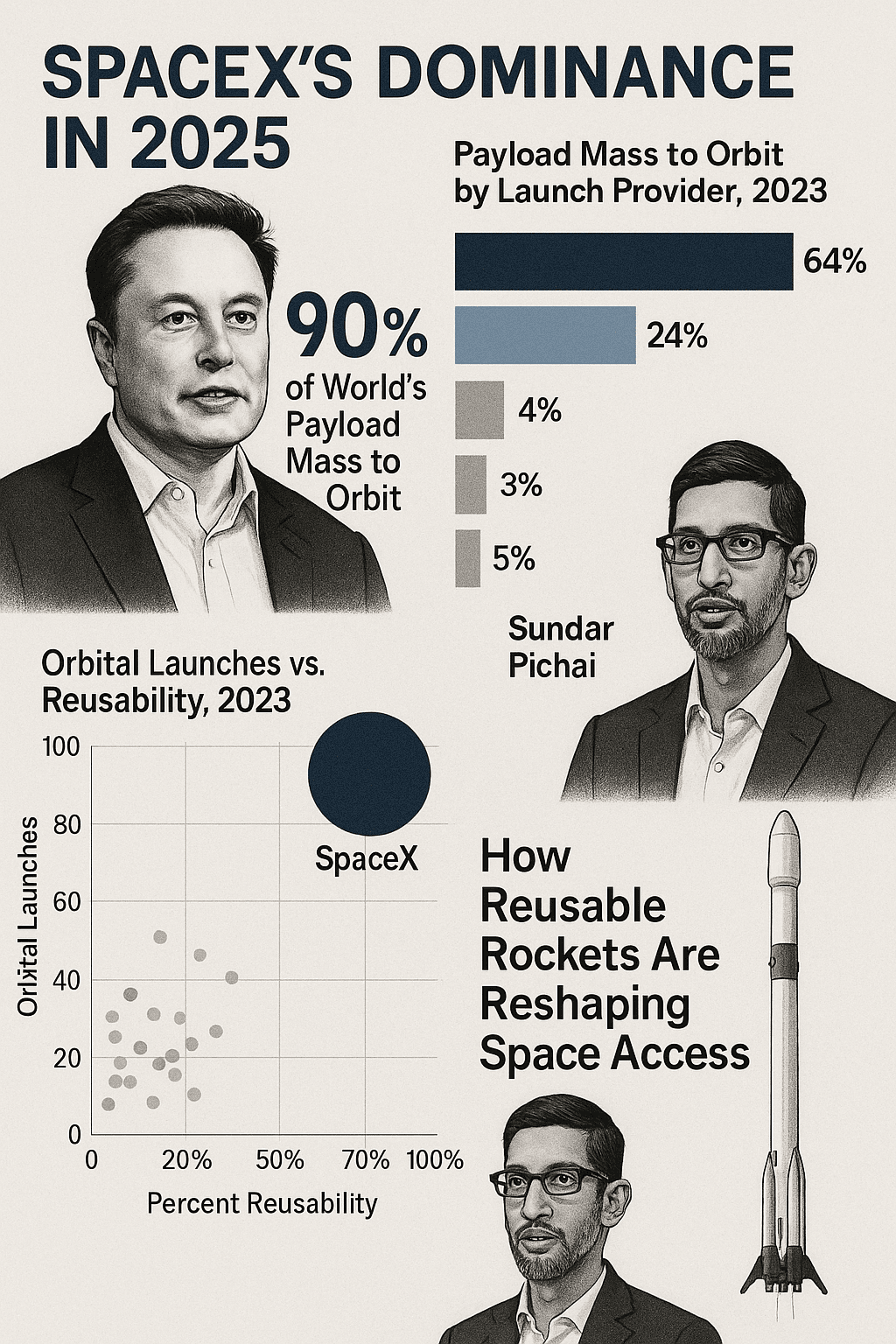
The familiar pang of COVID anxiety might be creeping back. News broke this week that NB.1.8.1, the fast-spreading variant fueling a significant surge in hospitalizations across China, has officially landed on US soil. While experts stress it’s likely less deadly than earlier strains, concerns about its contagiousness and potential to dodge our immune defenses are putting public health officials on alert. Let’s unpack what we know about this latest chapter in the pandemic story.
The Variant Arrives: Detected at US Airports
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the presence of NB.1.8.1 through its robust airport surveillance program. Travelers arriving at major US entry points – including airports in California, Washington State, Virginia, and New York City – tested positive for the variant between late March and early April. Reports from the New York Post indicate additional cases have been identified in Ohio, Rhode Island, and Hawaii.
While the current number of detected NB.1.8.1 cases within the US remains relatively low and geographically scattered (making comprehensive tracking difficult for the CDC right now), the very fact it’s here, carried by international travelers from diverse locations, signals its ability to cross borders with ease.
🧬 Symptoms
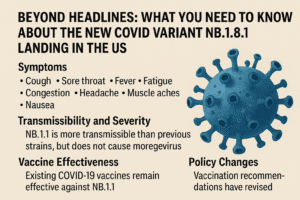
The symptoms associated with NB.1.8.1 are similar to those of previous variants, including:
Sore throat
Fatigue
Mild cough
Fever
Muscle aches
Nasal congestion
Headache
Nausea
Loss of appetiteNavbharat Times+1San Francisco Chronicle+1New York Post+2Home – Thailand Medical News+2San Francisco Chronicle+2Home – Thailand Medical News+6San Francisco Chronicle+6Home – Thailand Medical News+6Anadolu AjansıHome – Thailand Medical News
Additionally, some patients have reported persistent low-grade hyperthermia—a condition where the body temperature is elevated beyond normal without the typical fever response
Why the Concern? Contagion and Evasion
So, what makes NB.1.8.1 stand out?
High Contagiousness: Scientists are observing a clear “growth advantage” compared to other circulating variants. “It appears to have a growth advantage, suggesting it may spread more easily,” stated Dr. Subhash Verma, a microbiology and immunology professor at the University of Nevada, to CBS News. This means it could become dominant more quickly.
Potential Vaccine Evasion: Early data suggests NB.1.8.1 might be better at slipping past the immunity provided by prior vaccination or infection. This doesn’t mean vaccines are useless – they still offer crucial protection against severe illness – but it could lead to more breakthrough infections.
Less Severe (But Still Serious): Crucially, experts emphasize there’s no current evidence that NB.1.8.1 causes more severe disease or higher death rates than recent Omicron subvariants. This aligns with the trend of the virus evolving towards greater transmissibility but lower intrinsic severity. However, its ability to infect more people rapidly can still lead to concerning spikes in hospitalizations, especially among vulnerable populations.
The View from China and Hong Kong: A Surge Unfolding
NB.1.8.1 isn’t a theoretical threat overseas; it’s causing real disruption. It has rapidly become the dominant strain in China, driving significant increases in emergency room visits and hospital admissions nationwide.
Hong Kong offers a stark snapshot. Authorities are reporting their worst COVID surge in at least a year, directly attributed to NB.1.8.1. Within a recent four-week period, they recorded 81 severe cases and 30 deaths, predominantly among seniors aged 65 and older.
“What they’re seeing in China, Hong Kong and some other areas where this variant has really surged, is an increase in hospitalization,” confirmed Dr. Amy Edwards of Case Western Reserve University’s medical school to CBS News. This highlights the risk high transmission poses to healthcare systems and the elderly, even with a potentially less virulent virus.
Global Footprint: More Than Just China-US Travel
The CDC’s airport screening revealed an important detail: travelers carrying NB.1.8.1 hadn’t only come directly from China. They had recently passed through Japan, South Korea, France, Thailand, Vietnam, Spain, and the Netherlands. This paints a picture of a variant with a broad and established global footprint, likely circulating more widely than current detection systems can fully capture. It underscores the interconnectedness of our world and the constant potential for viral spread.
A Shift in US Policy: Vaccines for Kids and Pregnant Women
Amidst news of this emerging variant, another significant development unfolded in US COVID policy. Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., alongside FDA Commissioner Marty Makary and NIH Director Jay Bhattacharya, announced the removal of routine COVID-19 vaccinations from the CDC’s recommended immunization schedule for healthy children and pregnant women.
Kennedy stated in a social media video that he made this decision, though notably, no CDC officials appeared in the announcement. The CDC referred questions to Kennedy and the Department of Health and Human Services.
This move has drawn criticism and concern from some public health experts. Dr. Michael Osterholm, director of the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy, called it “concerning and confusing,” stating, “There’s no new data or information, just them flying by the seat of their pants.”
It’s crucial to note that COVID-19 remains a serious threat. While children are generally at lower risk, CDC data shows the virus has been the underlying cause of more than 1,300 childhood deaths in the US since the pandemic began. The vast majority of the nation’s over 1.2 million COVID deaths have been among the elderly.
Staying Informed, Not Panicked: The Path Forward
The detection of NB.1.8.1 in the US is a reminder that COVID-19 continues to evolve and circulate globally. Here’s how to navigate this latest development:
Don’t Panic, But Be Aware: NB.1.8.1 is here, likely more contagious, but not currently indicated to be more severe. Vigilance, not alarm, is key.
Prioritize Protection for the Vulnerable: If you are elderly, immunocompromised, or have underlying health conditions, ensure your vaccinations are up-to-date. Discuss preventative measures like Paxlovid with your doctor if infected.
Consider Personal Risk: In crowded indoor settings or during periods of high community spread (which NB.1.8.1 could fuel), wearing a high-quality mask (N95/KN95) remains a powerful tool.
Stay Updated on Vaccines: While policy shifts occur, consult your personal physician about the best COVID vaccination strategy for you and your family based on individual health risks. Vaccine recommendations can change as new variants emerge and more data is collected.
Test if Symptomatic or Exposed: If you feel sick or know you’ve been exposed, test promptly. Early detection helps manage the illness and prevent spread.
Follow Reputable Sources: Rely on the CDC, WHO, and trusted medical institutions for updates on NB.1.8.1 and COVID-19 guidance.
💉 Vaccine Efficacy and Policy Changes
While existing vaccines continue to offer protection against severe disease, NB.1.8.1’s mutations may reduce their effectiveness in preventing infection. In response, U.S. health authorities are considering policy adjustments, potentially limiting booster recommendations to seniors and high-risk groups, and reevaluating guidance for healthy children and pregnant women
✅ Preventive Measures
To mitigate the spread of NB.1.8.1, health experts recommend:
Wearing masks in crowded or enclosed spaces
Practicing good hand hygiene
Avoiding close contact with symptomatic individuals
Staying home when experiencing symptoms
Considering updated booster vaccinations, especially for vulnerable populations
🌍 Global Spread and Impact
Following significant outbreaks in China, NB.1.8.1 has spread to various parts of Asia and Europe. In Taiwan, nearly 6,000 individuals sought medical attention in a single week due to this variant, marking a 78% increase from the previous week. In the U.S., cases have been identified among international travelers and have since appeared in multiple states
The arrival of NB.1.8.1 is another twist in the long COVID narrative. It reinforces that the virus isn’t gone; it’s simply changed its tactics. By staying informed, focusing on protecting the most vulnerable, and using the tools we have wisely – vaccines, masks, testing, and treatment – we can manage this latest variant without losing the hard-won ground we’ve gained. Keep an eye on the data, listen to your body, and consult your doctor, not just headlines, for your personal health decisions.